Alex Arianna during a reading lesson at Lincoln Elementary School. (Photo courtesy Frederick County Public Schools)
Alice Tickler tries to stay positive when it comes to educating young children, but the longtime teacher admits there are some things that can make it hard — and it’s not anything the students do.
Things like the legislature’s failure to fund a training program, specifically for reading and math teachers. As a teacher for 28 years, she’s seen the benefits of what educators call a “coaching program.”
“Seeing other teachers in action, having a mentor teacher that knows how to teach reading alongside of you or coaching you, that’s huge,” said Tickler, a first-grade teacher in Queen Anne’s County public schools. “That coaching model would really benefit teachers.”
Tickler’s comments echo recommendations in a report being released Tuesday morning by Maryland READS, a nonprofit focused on the improvement of reading instruction. Providing consistent funding for teachers is just one of the recommendations in “The State of Reading in Maryland 2025: It’s Time for a Comeback after a Decade of Decline.”
While the General Assembly approved the Excellence in Maryland Public Schools Act last week without funding for a training program, it did approve funding for a national teacher recruitment campaign and a $2,000 relocation grant to “incentivize an out-of-state licensed teacher to move to the state.”
The report’s not all about funding, however, and acknowledges the state’s financial difficulties. Similar to a report produced last year, Tuesday’s document outlines recommendations to improve literacy, such as businesses providing employees time to serve as local tutors, and state and local leaders organizing town halls on digital education for families.
Because of the state’s fiscal challenges, the report suggests philanthropists provide financial and other resources to help create “thriving, reading ecosystems.”
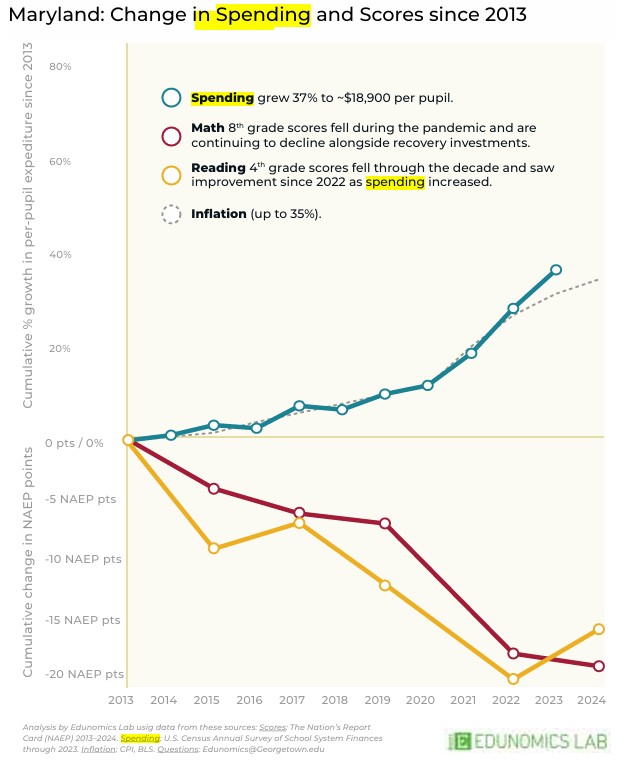
A chart shows per pupil spending increased in comparison to test scores for fourth- and eighth-grade students in Maryland. (Chart courtesy of Maryland READS)
According to the report, per pupil spending increased by 37% since 2013 through last year. During that time, National Assessment of Educational Progress math scores have constantly declined.
“Everything the state has done to put a system of support in place … gives us hope,” Trish Brennan-Gac, executive director of Maryland READS, said in an interview. “But I think the legislature needs to get on board a little bit more and trust her [State Superintendent Carey Wright] leadership because she has a proven track record, and I don’t think they did that this time around.”
‘Make sure children can read’
Tuesday’s document notes a report last year from the National Council on Teacher Quality. It gave Maryland and 19 other states an overall “moderate” rating on teacher training programs based on five policy actions to strengthen implementation of the “science of reading,” which Wright utilized as public schools leader in Mississippi and pushed to incorporate in Maryland.
The council gave three ratings – strong, moderate and weak – not only for the total assessment of training programs, but also separate reviews of each policy action. On the policy statement, “Reviews teacher-preparation programs to ensure they teach the Science of Reading,” Maryland received a “weak” rating.
Maryland READS recommends the state Department of Education “should immediately exercise authority, including limiting grants and contracts, and hold Maryland teacher preparation programs accountable for aligning to Science of Reading by 2028.”
According to the report, what will help teachers with literacy instruction is an agreement the department made last year to implement a four-year, $6.8 million grant from the nonprofit Ibis Group of Washington, D.C.
About $5.3 million of that grant will be used for free online training in the science of reading for at least 30,000 paraprofessionals, teachers and other staff. The remaining $1.5 million would be for Johns Hopkins University and the department to research the impact of teacher efficacy, teacher background knowledge and literacy.
But Brennan-Gac said additional and consistent support is needed.
“Having a coach in the classroom actually helps the teacher change their practice,” Brennan-Gac said. “While it’s wonderful that we’ve brought these training programs into the state, [but] if they don’t get the coaching, we’re not really leveraging that wonderful resource we have and this whole movement that we’re doing.”
Some other recommendations from the report to improve literacy include:
Starting July 1, the department should collaborate with educators and organizations to begin work on drafting an adolescent literacy policy;The legislature should tie future funding to data related to proficiency rates at community schools, those that receive high concentration of poverty grants which provide a variety of wraparound and other services; andState, local and community leaders should educate parents and guardians on limiting the use of electronic devices for their children.
“We should do everything that we can to make sure that our children can read,” said Tickler, who serves on a statewide teacher advisory council created by the department this year. “We don’t want our children to enter that pipeline that takes them to jail or drugs. We want our kids to be successful and we want our kids to be literate.”
by William J. Ford, Maryland Matters
April 15, 2025
Maryland Matters is part of States Newsroom, a nonprofit news network supported by grants and a coalition of donors as a 501c(3) public charity. Maryland Matters maintains editorial independence. Contact Editor Steve Crane for questions: [email protected].